Minchinhampton Academy pupils share climate change fears
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
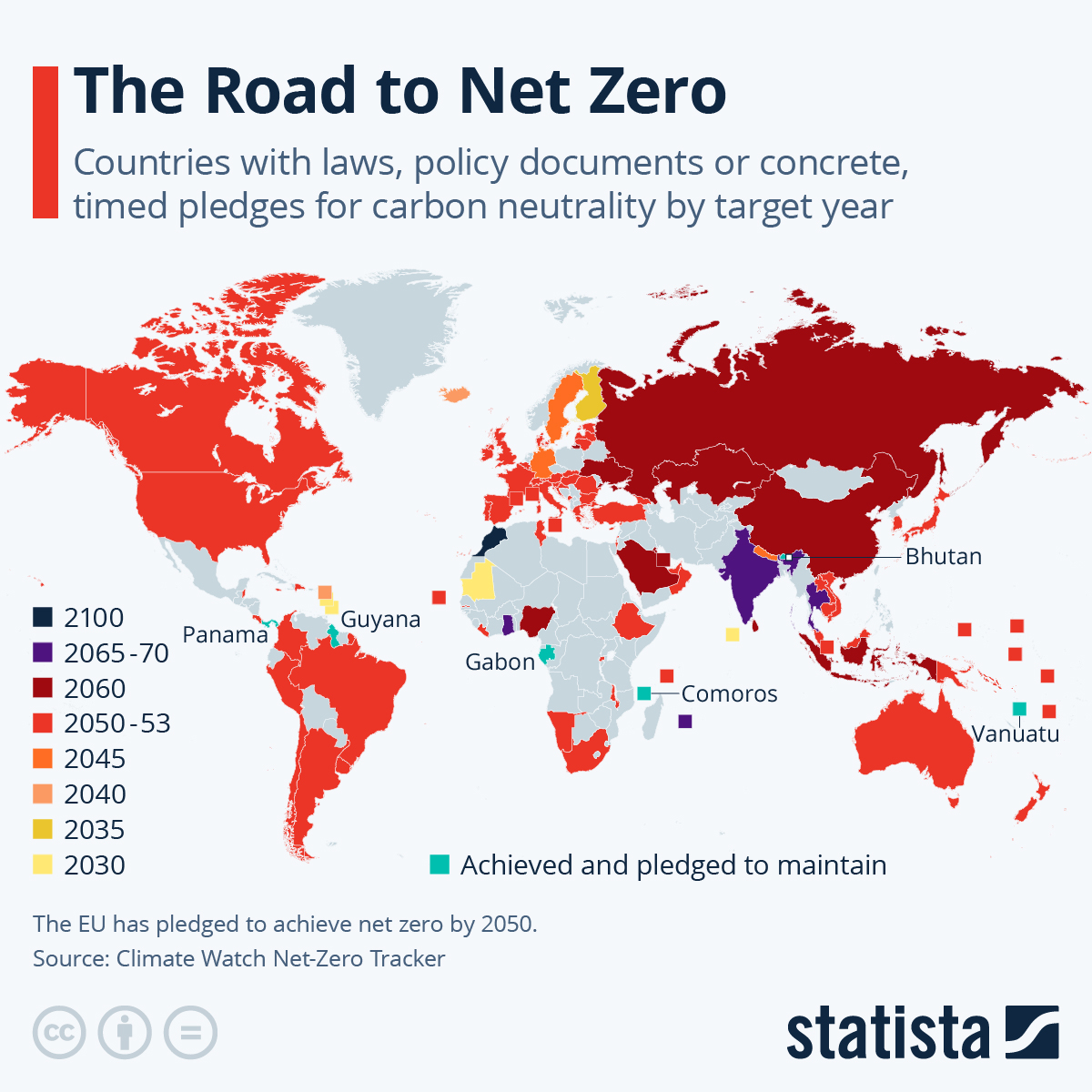
One of the main aims of the major climate conference is to secure global net-zero by mid-century – but some countries are considerably further ahead in the race to beat the climate disaster than others. Leading the road to net-zero among larger countries Finland, which aims to become carbon neutral by 2035 – the earliest goal set in the continent.
Elsewhere in Europe, Iceland and Austria are looking to reach net-zero by 2040, with Germany and Sweden pushing the date for carbon neutrality to 2045.
The UK currently has a target of 2050 – but for many countries, these targets could be accelerated following COP26.
Most of the countries with climate pledges have put down 2050 as their goal, with the notable exception of China, India and Russia, all of which are targeting 2060 for net-zero emissions.
Only two countries in the world have already managed to reach net-zero so far – Suriname and Bhutan – and could even go as far as having a net negative carbon economy in the next few years.

What does net zero mean?
Net-zero means achieving a balance between the greenhouse gases put into the atmosphere and those taken out.
Reaching net-zero requires significant abatement of greenhouse gas emissions across all sectors of the economy – with some changes easier to make than others.
For example, the switch from fuel to electric cars is largely quite simple, in comparison to reforming air travel so that it doesn’t emit harmful gases.

Why is net-zero so important?
Climate change is destroying the planet, and scientists have concluded that global emissions need to reach net-zero around mid-century to give a reasonable chance of limiting warming to 1.5C.
Warming of over 2C will see 70 percent of coastlines change across the world, as well as significantly increase the likelihood of frequent severe heatwaves, among other things.
An increase of 1C to 2C may not sound like much, but the world is already starting to see the devastating effects of global warming, with the melting of Polar ice, rising sea levels, animal species going extinct and more extreme weather conditions leading to floods, droughts, hurricanes and typhoons.
If the temperature continues to increase, these will worsen, putting humans and animals at risk.
Essentially, this means carbon emissions must stop, not simply be reduced.
DON’T MISS
Extinction Rebellion chaos as major UK oil refinery BLOCKED [REPORT]
China, Europe and India admit they need Russian fossil fuels [INSIGHT]
COP26 protests: All the protests and road closures taking place [EXPLAINER]

How will the UK achieve net-zero?
There are two main ways of reaching net-zero – reducing existing emissions and actively removing greenhouse gases.
Reducing emissions needs to be tackled in a number of ways – from decreasing reliance on coal and oil and moving reliance onto electricity, as well as making homes efficient, and tackling poor agricultural practices.
Rewilding and planting also helps with reaching net-zero, as plants remove Co2 from the atmosphere.
The past five years have been the hottest on record since 1850, according to a recent report by the UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC).
A new poll has shown the British public is actually in favour of a referendum on the Government’s net-zero proposals.
Of adults surveyed, 42 percent said they supported a vote on the plan, whilst 30 percent opposed it, and 28 percent did not declare a preference, according to a YouGov survey conducted this month.
When the “don’t knows” were excluded from the results, a majority of 58 per cent wanted a ballot on the issue.
Source: Read Full Article