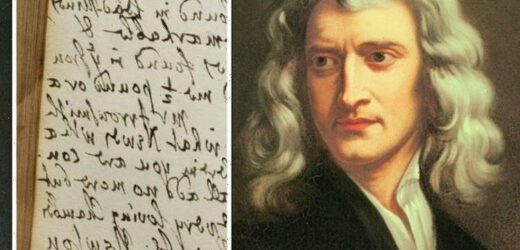NORAD unveils the history of their Santa Claus tracker
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
The letters were addressed to John Wickins, his long-time assistant at Cambridge University, and runs contrary to the popular idea of Newton being an introverted scholar who lived in isolation. Mr Wickins lived with the famous mathematician at Trinity College between 1665 and 1683. He served as an unpaid assistant or amanuensis.
He would copy Newton’s notes and source materials for the pair’s experiments in their rooms, which were converted into a laboratory.
He is also referenced by name in Newton’s telescope, built-in 1678.
The Newton-Wickins reflector is regarded the most accurate of the three designed by Newton, in large part due to Wickins’ contribution on its mirror.
Academics have recently discovered the relationship between the two went further than just that of a mathematician and his assistant.


Some of the letters are fairly standard for what researchers know about the scholar.
In one letter addressed to Wickins, he instructs his assistant to source “transparent stones” growing on iron for their telescope.
In another, dated July 19, 1677, he ranted about his ongoing dispute with a Jesuit priest over his particle theory of light and threatened to “lay open” one of the priest’s students.
In another letter, dated Aug 19, 1682, Newton lamented the difficulty of recommending books to Wickins, writing: “For what pleases me may not after Perusal please you & then they will be but lumber to you.”

Researchers believe Mr Wickins was Newton’s only friend at Cambridge, with the former paying for his “dividends and chamber rent” and later leaving behind his furniture and a wooden pint flagon after leaving Trinity.
According to Scott Mandelbrote, the editorial director of the Newton Project and Fellow of Peterhouse at Cambridge University, the letters show Newton was “not living in isolation from people around him” and was “willing to share things with people”.
He said: “We have tended to think of Newton as very much a kind of lone genius, the man whose lectures nobody went to, the man whose ideas were so difficult that none of his contemporaries in Cambridge could understand him, which is really a misrepresentation.
“He is discussing things with friends and is willing to involve friends and contemporaries in thinking together about problems, and is willing to take advice from people who he comes in daily contact with.”
DON’T MISS:
Djokovic shamed by UK scientist after anti-vax star sparks chaos [SPOTLIGHT]
Omicron warning issued as ‘organ complications’ linked to Covid [REVEAL]
WHO issues urgent Omicron warning: ‘Calling it mild is a mistake!’ [INSIGHT]


Historians have previously suggested Newton may have been a repressed homosexual, based on letter to the Swiss mathematician Nicholas Fatio de Duillier.
In one letter, Mr Duillier wrote: “I could wish sir to live all my life, or the greatest part of it, with you.”
In his correspondence with Wickins, he referred to his assistant as “your very loving Chamberfellow”.
However, Mr Mandelbrote dismissed that particular sign-off, saying that it was in keeping with the times and spoke to the pair’s shared intellectual curiosity.
Source: Read Full Article