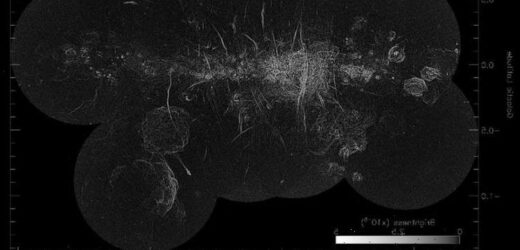
Milky Way radio signals visualised by The University of Sydney
We use your sign-up to provide content in ways you’ve consented to and to improve our understanding of you. This may include adverts from us and 3rd parties based on our understanding. You can unsubscribe at any time. More info
Researchers were able to capture an unprecedented telescopic image of the Milky Way galaxy’s turbulent centre and have exposed nearly 1,000 mysterious strands dangling in space. These one-dimensional filaments stretch up to 150 light-years long and are seen in pairs or clusters. often stacked equally spaced, side by side like strings on a harp.
Northwestern University’s Farhad Yusef-Zadeh, the paper’s lead author, was the first to find the highly organized, magnetic filaments in the early 1980s.
He discovered that the mysterious strands are comprised of cosmic-ray electrons gyrating the magnetic field at close to the speed of light.
However, the origin of these filaments has remained an unsolved mystery ever since.
The new images have exposed 10 times more filaments than were previously discovered, enabling the researchers to conduct statistical studies across a wide population of filaments for the first time.


This information potentially could help them finally unravel the long-standing mystery of the filament’s origins.
Prof Yusef-Zadeh said: “We have studied individual filaments for a long time with a myopic view.
“Now, we finally see the big picture — a panoramic view filled with an abundance of filaments.
“Just examining a few filaments makes it difficult to draw any real conclusion about what they are and where they came from.

“This is a watershed in furthering our understanding of these structures.”
To construct the image with unprecedented clarity and detail, astronomers spent three years observing and analyzing data at the South African Radio Astronomy Observatory (SARAO).
After spending 200 hours on SARAO’s MeerKAT telescope, researchers pieced together a mosaic of 20 separate observations of different sections of the sky toward the centre of the Milky Way galaxy, 25,000 light-years from Earth.
Along with the filaments, the image also captures radio emissions from a number of different phenomena, including outbursting stars, stellar nurseries and new supernova remnants.
DON’T MISS:
Putin furious as Germany BANS Russian gas and signs deal with Ukraine [SPOTLIGHT]
Turkey forced to CUT power and be plunged into darkness [REVEAL]
Calls for Plan B restrictions after surge in Omicron mutation cases [INSIGHT]


Oxford University astrophysicist Ian Heywood said: “I’ve spent a lot of time looking at this image in the process of working on it, and I never get tired of it.
“When I show this image to people who might be new to radio astronomy, or otherwise unfamiliar with it, I always try to emphasize that radio imaging hasn’t always been this way, and what a leap forward MeerKAT really is in terms of its capabilities.
“It’s been a true privilege to work over the years with colleagues from SARAO who built this fantastic telescope.”
To obtain a more detailed picture of the filaments, the researchers used a technique to remove the background from the main image in order to isolate the strands from the surrounding structures.
The resulting picture astounded Prof Yusef-Zadeh, as he described it as “modern art”.
He added: “These images are so beautiful and rich, and the mystery of it all makes it even more interesting.”
Source: Read Full Article